Unveiling the Tapestry of California’s Indigenous Heritage: A Guide to Native Tribes on a Map
Unveiling the Tapestry of California’s Indigenous Heritage: A Guide to Native Tribes on a Map

California, a land of diverse landscapes and vibrant culture, holds a rich history interwoven with the stories of its indigenous peoples. For centuries, Native tribes have called this land home, shaping its environment, traditions, and spirit. Today, their legacy continues to inspire and inform, reminding us of the profound connection between people and place.
This article serves as a guide to understanding the diverse tapestry of California’s Native tribes, offering a glimpse into their history, culture, and current presence. We’ll explore their geographical distribution, their unique languages and traditions, and the challenges they face in preserving their heritage.
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of California’s Indigenous Heritage: A Guide to Native Tribes on a Map
- Uncover the Spirit of the Cheyenne: Unveiling the Power of the Sacred Totem
- The Wealthiest Tribe in Africa: A Glittering Legacy
- Bears: Sacred Guardians of Native American Heritage
- Discover the Washte Tribe’s Enduring Legacy: A Journey Through Time
- Unlocking the Mysteries: Discover Ancient Pueblo Sites!
A Map of California’s Native Tribes: A Visual Journey
To truly appreciate the depth and breadth of California’s indigenous heritage, a map becomes an essential tool. It allows us to visualize the geographical distribution of different tribes, revealing the intricate mosaic of cultures that have thrived across the state.
Key Features of a California Native Tribes Map:
- Tribal Territories: The map should clearly delineate the traditional territories of each tribe, providing a visual representation of their historical presence.
- Tribal Names: Each tribe should be labeled with its correct name, honoring its identity and acknowledging its unique cultural heritage.
- Language Families: The map should indicate the language family each tribe belongs to, showcasing the linguistic diversity that once characterized California.
- Modern Reservations: The map should highlight the locations of current reservations, recognizing the ongoing presence of Native tribes in California.
- Cultural Sites: Important cultural sites, such as archaeological locations, sacred grounds, and traditional gathering places, should be marked, offering a glimpse into the rich history and cultural significance of these locations.
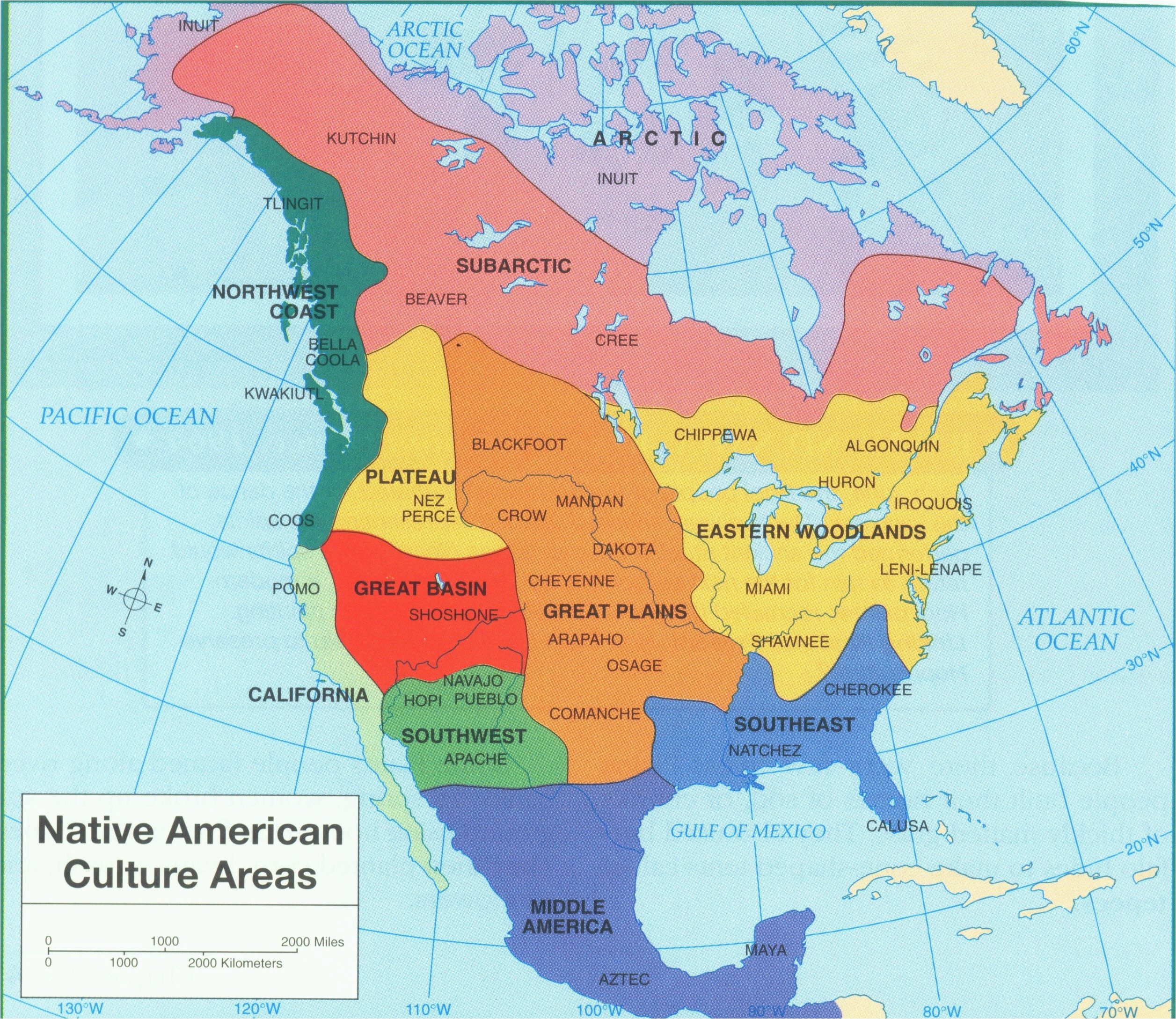
Understanding the Diversity: A Glimpse into California’s Native Tribes
California boasts a remarkable diversity of Native tribes, each with its own unique language, traditions, and cultural practices. While a comprehensive overview is impossible in this article, we can explore some prominent tribes and their contributions to California’s history and culture:
1. The Chumash:
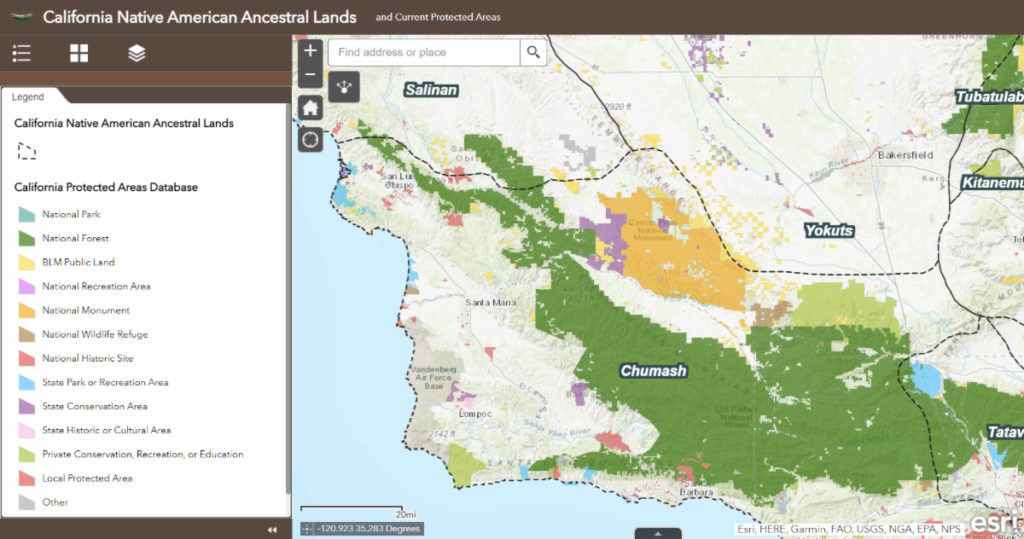
- Location: Southern California, along the coast from Santa Barbara to Malibu.
- Language: Chumash, a language isolate, meaning it is not related to any other known language.
- Culture: Known for their intricate basketry, their use of the ocean for sustenance, and their complex social structures.
- Notable Contributions: The Chumash developed a sophisticated system of navigation and resource management, leaving behind remarkable cave paintings and rock art.

2. The Miwok:
- Location: Central California, particularly in the Sierra Nevada foothills and the Sacramento Valley.
- Language: Miwok, part of the Hokan language family.
- Culture: Known for their skilled basket weavers, their use of acorns as a staple food, and their strong connection to the natural world.
- Notable Contributions: The Miwok developed unique forms of storytelling, dance, and music, leaving behind a rich oral tradition.
3. The Pomo:
- Location: Northern California, along the coast from Sonoma County to Mendocino County.
- Language: Pomo, part of the Pomoan language family.
- Culture: Known for their elaborate beadwork, their use of obsidian for tools and weapons, and their sophisticated knowledge of medicinal plants.
- Notable Contributions: The Pomo developed unique forms of basketry, weaving, and pottery, leaving behind a legacy of artistic expression.
4. The Karuk:
- Location: Northwestern California, along the Klamath River.
- Language: Karuk, part of the Athabaskan language family.
- Culture: Known for their intricate knowledge of the natural world, their use of salmon for sustenance, and their elaborate ceremonies.
- Notable Contributions: The Karuk developed a unique system of resource management, ensuring the sustainability of their environment.
5. The Yurok:
- Location: Northwestern California, along the Klamath River.
- Language: Yurok, a language isolate.
- Culture: Known for their highly developed social structure, their use of redwood for housing and canoes, and their intricate ceremonies.
- Notable Contributions: The Yurok developed a unique form of law and government, based on consensus and respect for the environment.
The Enduring Legacy: Challenges and Resilience
Despite their rich history and cultural contributions, California’s Native tribes have faced significant challenges throughout history. Colonialism, forced assimilation, and the loss of traditional lands have had a devastating impact on their communities.
However, despite these challenges, Native tribes in California have shown remarkable resilience. They continue to fight for their rights, preserve their traditions, and advocate for their communities.
Key Challenges Faced by California’s Native Tribes:
- Loss of Land and Resources: The forced removal of Native tribes from their traditional territories and the loss of access to vital resources have had a profound impact on their cultures and livelihoods.
- Assimilation Policies: Government policies aimed at assimilating Native tribes into mainstream society have led to the suppression of their languages, traditions, and cultural practices.
- Discrimination and Prejudice: Native tribes continue to face discrimination and prejudice, leading to disparities in education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
- Environmental Degradation: The destruction of sacred sites, the pollution of traditional waterways, and the loss of biodiversity have had a devastating impact on the environment and the cultural heritage of Native tribes.
Preserving the Past, Shaping the Future: The Role of Education and Awareness
To ensure the continued survival and thriving of California’s Native tribes, it is essential to promote education and awareness about their history, culture, and current challenges.
Ways to Support California’s Native Tribes:
- Educate Yourself: Learn about the history and culture of Native tribes in California. Visit museums, attend cultural events, and read books and articles written by Native authors.
- Support Native Businesses: Patronize Native-owned businesses, restaurants, and cultural centers.
- Advocate for Native Rights: Support organizations that advocate for the rights of Native tribes, such as the California Native American Heritage Commission.
- Respect Cultural Practices: Be mindful of the cultural sensitivities of Native tribes and avoid appropriating their traditions or artifacts.
- Engage in Dialogue: Participate in conversations about the history and legacy of Native tribes, fostering understanding and respect.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Resilience and Hope
The map of California’s Native tribes is a testament to their enduring legacy, their resilience in the face of adversity, and their ongoing efforts to preserve their cultures and traditions. By understanding their history, appreciating their contributions, and supporting their communities, we can help ensure that their voices are heard and their heritage is honored.
As we explore the tapestry of California’s indigenous heritage, we are reminded of the importance of recognizing and respecting the diversity of cultures that have shaped this state. By embracing the stories of the past, we can build a future where all Californians, Native and non-Native alike, can thrive together in harmony.
FAQ: Native Tribes in California
Q: How many Native tribes are there in California?
A: There are over 100 federally recognized Native tribes in California.
Q: What is the largest Native tribe in California?
A: The largest federally recognized tribe in California is the Cherokee Nation, with a significant population residing in the state.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing Native tribes in California today?
A: Native tribes in California face numerous challenges, including:
- Loss of land and resources: Historical land dispossession and ongoing development pressures continue to impact their access to traditional territories and resources.
- Discrimination and prejudice: Native communities continue to experience systemic discrimination and prejudice, leading to disparities in healthcare, education, and economic opportunities.
- Cultural preservation: Maintaining their languages, traditions, and cultural practices in the face of assimilation pressures remains a significant challenge.
- Environmental degradation: The impact of pollution, climate change, and development on their traditional lands and sacred sites poses a threat to their cultural heritage and well-being.
Q: How can I learn more about Native tribes in California?
A: There are many ways to learn more about Native tribes in California:
- Visit museums: The California Indian Museum and Cultural Center in Sacramento and the Autry Museum of the American West in Los Angeles offer exhibits and programs showcasing Native cultures.
- Attend cultural events: Many tribes hold powwows and other cultural events throughout the year, providing opportunities to experience their traditions firsthand.
- Read books and articles: Numerous books and articles have been written about Native tribes in California, offering insights into their history, culture, and current challenges.
- Support Native organizations: Organizations such as the California Native American Heritage Commission and the American Indian Movement advocate for Native rights and provide resources for education and cultural preservation.
Q: What are some ways I can support Native tribes in California?
A: You can support Native tribes in California by:
- Educating yourself: Learn about their history, culture, and current challenges.
- Supporting Native businesses: Patronize Native-owned businesses, restaurants, and cultural centers.
- Advocating for Native rights: Support organizations that advocate for the rights of Native tribes.
- Respecting cultural practices: Be mindful of the cultural sensitivities of Native tribes and avoid appropriating their traditions or artifacts.
- Engaging in dialogue: Participate in conversations about the history and legacy of Native tribes, fostering understanding and respect.
By learning about and supporting Native tribes in California, we can help ensure that their voices are heard and their heritage is honored.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of California’s Indigenous Heritage: A Guide to Native Tribes on a Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!