Unveiling the Legacy: Exploring the Largest Native American Tribes in the US
Unveiling the Legacy: Exploring the Largest Native American Tribes in the US

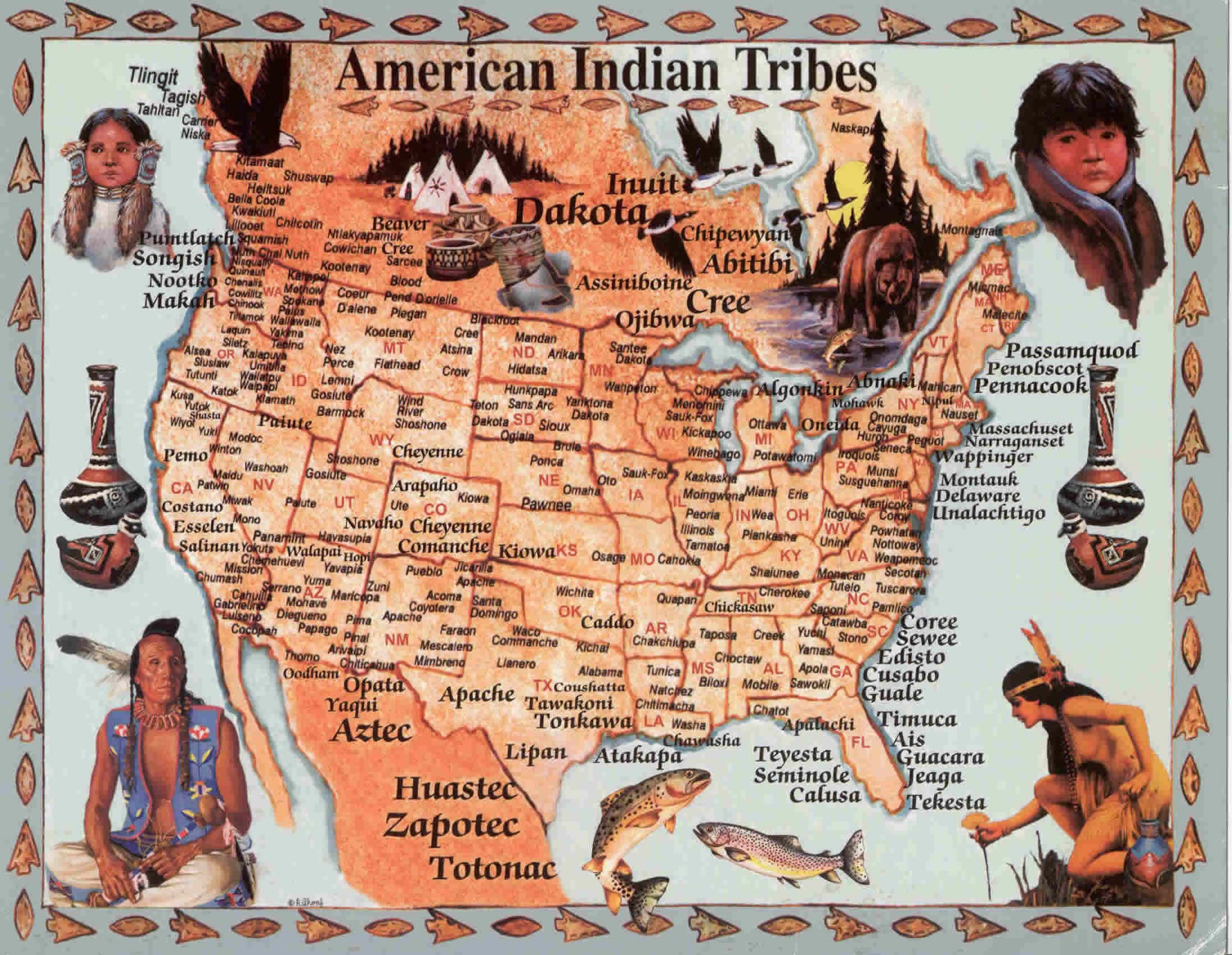
The United States, a nation built upon a rich tapestry of cultures, boasts a vibrant and resilient Native American population. Though often overlooked in mainstream narratives, the contributions and legacies of indigenous tribes continue to shape the country’s social, cultural, and political landscapes. This article delves into the story of some of the largest Native American tribes in the US, shedding light on their history, traditions, and contemporary struggles.
A Brief History: Understanding the Context
Related Articles: Unveiling the Legacy: Exploring the Largest Native American Tribes in the US
- Lakota People’s Law Project: Empowering Indigenous Rights & Justice!
- Unraveling the Meaning of Forrest Gump’s Feather: Symbolic Significance Explored
- Untold Stories: Rediscovering the Fierce Spirit of Blackfoot – Native American Legends
- Drumbeats of Native American Spirits: Echoes of Sacred Rhythms
- Feather Art Ideas: Unleash Your Creativity with Exquisite Designs
Before European colonization, North America was home to hundreds of distinct indigenous nations, each with its own unique language, culture, and governance system. However, the arrival of European settlers brought about a devastating period of displacement, forced assimilation, and cultural suppression. The Trail of Tears, the Indian Removal Act, and the ongoing struggle for land rights are stark reminders of the injustices faced by Native Americans throughout history.
Despite these challenges, indigenous communities have shown remarkable resilience. They have fought to preserve their languages, traditions, and cultural identities, passing down their heritage to future generations. Today, the largest Native American tribes in the US represent a powerful testament to this enduring spirit.
The Cherokee Nation: Guardians of the Southeastern Woodlands
With a population exceeding 380,000, the Cherokee Nation is the largest federally recognized tribe in the United States. Originally residing in the southeastern woodlands, the Cherokee developed a complex social and political structure, renowned for their oral traditions, storytelling, and intricate beadwork. Their language, Cherokee, is a unique syllabary system, a testament to their advanced linguistic development.
The Cherokee Nation’s history is intertwined with the tragic story of the Trail of Tears, a forced relocation in the 1830s that saw thousands of Cherokee people driven from their ancestral lands to present-day Oklahoma. Despite this hardship, the Cherokee Nation has persevered, rebuilding their community and establishing a strong tribal government. Today, the Cherokee Nation operates a thriving economy, focusing on education, healthcare, and cultural preservation.
The Navajo Nation: Keepers of the Southwest Landscape
The Navajo Nation, with a population exceeding 170,000, is the largest federally recognized tribe by land area, spanning over 27,000 square miles across Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. Known for their intricate weaving, silverwork, and storytelling, the Navajo people have a deep connection to the land, their culture deeply intertwined with the arid landscape of the Southwest.
The Navajo Nation’s history is marked by resilience in the face of hardship. During World War II, thousands of Navajo Code Talkers utilized their language to create an unbreakable code, playing a crucial role in Allied victories in the Pacific Theater. Today, the Navajo Nation continues to face challenges related to poverty, healthcare, and environmental issues, but they remain committed to preserving their cultural heritage and advocating for their rights.

The Choctaw Nation: The Heart of the Southeastern Woodlands
The Choctaw Nation, with a population exceeding 200,000, is the third largest federally recognized tribe in the United States. Known for their rich musical traditions, intricate pottery, and their role in the development of the "Choctaw language," they are deeply rooted in the southeastern woodlands.
The Choctaw Nation’s history is marked by both hardship and resilience. They were forcibly relocated to Oklahoma during the Trail of Tears, but they rebuilt their community, establishing a strong tribal government and advocating for their rights. Today, the Choctaw Nation is focused on economic development, education, and healthcare, while also working to preserve their cultural heritage.
The Chickasaw Nation: A Legacy of Innovation and Resilience
The Chickasaw Nation, with a population exceeding 100,000, is a proud and thriving tribe with a rich history and a vibrant present. Originally residing in the southeastern woodlands, the Chickasaw people were known for their skilled craftsmanship, particularly in pottery and basketry. They also developed a complex social structure and a strong sense of community.

The Chickasaw Nation’s journey has been marked by both hardship and triumph. They were forcibly relocated to Oklahoma during the Trail of Tears, but they persevered, rebuilding their community and establishing a strong tribal government. Today, the Chickasaw Nation is a leader in economic development, focusing on technology, healthcare, and education. They are also dedicated to preserving their cultural heritage and advocating for their rights.
The Muscogee (Creek) Nation: Keepers of the Southeastern Woodlands
The Muscogee (Creek) Nation, with a population exceeding 90,000, is a prominent tribe with a rich history and a strong cultural identity. Originally residing in the southeastern woodlands, the Muscogee (Creek) people were known for their agricultural skills, their intricate pottery, and their unique language. They also developed a complex social structure and a strong sense of community.
The Muscogee (Creek) Nation’s history is marked by both hardship and resilience. They were forcibly relocated to Oklahoma during the Trail of Tears, but they persevered, rebuilding their community and establishing a strong tribal government. Today, the Muscogee (Creek) Nation is focused on economic development, education, and healthcare, while also working to preserve their cultural heritage.
The Seminole Nation of Oklahoma: Guardians of the Florida Everglades

The Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, with a population exceeding 30,000, is a proud and resilient tribe with a unique history. Originally residing in the Florida Everglades, the Seminole people were known for their resistance to American expansion, fighting for their land and their way of life. They developed a unique culture, blending elements of their original Creek heritage with influences from African Americans and other indigenous groups.
The Seminole Nation’s history is marked by both hardship and triumph. They were forced to relocate to Oklahoma during the Indian Removal Act, but they persevered, rebuilding their community and establishing a strong tribal government. Today, the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma is focused on economic development, education, and healthcare, while also working to preserve their cultural heritage.
The Citizen Potawatomi Nation: A Legacy of Resilience and Innovation
The Citizen Potawatomi Nation, with a population exceeding 18,000, is a thriving tribe with a rich history and a vibrant present. Originally residing in the Great Lakes region, the Potawatomi people were known for their skilled craftsmanship, particularly in pottery and basketry. They also developed a complex social structure and a strong sense of community.
The Citizen Potawatomi Nation’s history is marked by both hardship and triumph. They were forcibly relocated to Oklahoma during the Indian Removal Act, but they persevered, rebuilding their community and establishing a strong tribal government. Today, the Citizen Potawatomi Nation is a leader in economic development, focusing on technology, healthcare, and education. They are also dedicated to preserving their cultural heritage and advocating for their rights.
The Osage Nation: Guardians of the Osage Hills
The Osage Nation, with a population exceeding 25,000, is a proud and resilient tribe with a rich history and a unique cultural identity. Originally residing in the Osage Hills of present-day Oklahoma, the Osage people were known for their skilled hunting and their complex social structure. They also developed a unique language and a strong sense of community.
The Osage Nation’s history is marked by both hardship and triumph. They were forcibly relocated to Oklahoma during the Indian Removal Act, but they persevered, rebuilding their community and establishing a strong tribal government. Today, the Osage Nation is focused on economic development, education, and healthcare, while also working to preserve their cultural heritage.
The Cheyenne and Arapaho Tribes: Guardians of the Great Plains
The Cheyenne and Arapaho Tribes, with a combined population exceeding 10,000, are two distinct tribes with a shared history and a strong cultural identity. Originally residing in the Great Plains, the Cheyenne and Arapaho people were known for their skilled horsemanship, their intricate beadwork, and their powerful warrior traditions. They also developed a complex social structure and a strong sense of community.
The Cheyenne and Arapaho Tribes’ history is marked by both hardship and triumph. They were forcibly relocated to Oklahoma during the Indian Removal Act, but they persevered, rebuilding their community and establishing a strong tribal government. Today, the Cheyenne and Arapaho Tribes are focused on economic development, education, and healthcare, while also working to preserve their cultural heritage.
Contemporary Challenges and Opportunities
Despite their resilience, the largest Native American tribes in the US continue to face challenges related to poverty, healthcare, education, and environmental issues. The legacy of colonization and forced assimilation continues to impact indigenous communities, creating disparities in access to resources and opportunities.
However, these tribes are also experiencing a period of renewed cultural revitalization and economic development. They are actively working to preserve their languages, traditions, and cultural identities, while also engaging in economic diversification and creating opportunities for their people.
Moving Forward: A Call for Understanding and Respect
Understanding the history, traditions, and contemporary challenges of the largest Native American tribes in the US is essential for fostering a more inclusive and equitable society. It is crucial to recognize the ongoing struggle for self-determination and to support the efforts of these tribes to preserve their cultural heritage and build a better future for their people.
By learning about the rich tapestry of Native American cultures, we can deepen our appreciation for the diversity of the United States and work towards a future where all people have the opportunity to thrive.
FAQs: Largest Native American Tribes in the US
1. What are the largest Native American tribes in the US?
The largest federally recognized tribes in the US are the Cherokee Nation, the Navajo Nation, the Choctaw Nation, the Chickasaw Nation, the Muscogee (Creek) Nation, the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Citizen Potawatomi Nation, the Osage Nation, and the Cheyenne and Arapaho Tribes.
2. How do these tribes maintain their cultural identities?
These tribes maintain their cultural identities through language revitalization programs, cultural events, traditional arts and crafts, and education initiatives that focus on indigenous knowledge and history.
3. What are some of the challenges faced by these tribes?
These tribes continue to face challenges related to poverty, healthcare, education, and environmental issues. They also face ongoing struggles for land rights and self-determination.
4. What are some of the opportunities for these tribes?
These tribes are experiencing a period of renewed cultural revitalization and economic development. They are actively working to preserve their languages, traditions, and cultural identities, while also engaging in economic diversification and creating opportunities for their people.
5. How can I learn more about Native American tribes?
You can learn more about Native American tribes by visiting tribal websites, museums, and cultural centers. You can also read books and articles about indigenous history and culture.
By engaging with the stories of the largest Native American tribes in the US, we can foster a deeper understanding of their resilience, their contributions to American society, and their ongoing struggle for self-determination. Let us work towards a future where all people are valued and respected, and where the rich tapestry of Native American cultures continues to thrive.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Legacy: Exploring the Largest Native American Tribes in the US. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!